A year and a half ago, I dropped out of one of the best computer science programs in Canada. I started creating my own data science master’s program
using online resources. I realized that I could learn everything I
needed through edX, Coursera, and Udacity instead. And I could learn it
faster, more efficiently, and for a fraction of the cost.
I’m
almost finished now. I’ve taken many data science-related courses and
audited portions of many more. I know the options out there, and what
skills are needed for learners preparing for a data analyst or data
scientist role. So I started creating a review-driven guide that recommends the best courses for each subject within data science.
For the first guide in the series, I recommended a few coding classes for the beginner data scientist. Then it was statistics and probability classes. Then introductions to data science. Also, data visualization.
Now onto machine learning.
For
this guide, I spent a dozen hours trying to identify every online
machine learning course offered as of May 2017, extracting key bits of
information from their syllabi and reviews, and compiling their ratings.
My end goal was to identify the three best courses available and
present them to you, below.
For
this task, I turned to none other than the open source Class Central
community, and its database of thousands of course ratings and reviews.
Since 2011, Class Central founder Dhawal Shah
has kept a closer eye on online courses than arguably anyone else in
the world. Dhawal personally helped me assemble this list of resources.
How we picked courses to consider
Each course must fit three criteria:
- It must have a significant amount of machine learning content. Ideally, machine learning is the primary topic. Note that deep learning-only courses are excluded. More on that later.
- It must be on-demand or offered every few months.
- It must be an interactive online course, so no books or read-only tutorials. Though these are viable ways to learn, this guide focuses on courses. Courses that are strictly videos (i.e. with no quizzes, assignments, etc.) are also excluded.
We believe we covered every notable course that fits the above criteria. Since there are seemingly hundreds of courses on Udemy, we chose to consider the most-reviewed and highest-rated ones only.
There’s
always a chance that we missed something, though. So please let us know
in the comments section if we left a good course out.
How we evaluated courses
We
compiled average ratings and number of reviews from Class Central and
other review sites to calculate a weighted average rating for each
course. We read text reviews and used this feedback to supplement the
numerical ratings.
We made subjective syllabus judgment calls based on three factors:
- Explanation of the machine learning workflow. Does the course outline the steps required for executing a successful ML project? See the next section for what a typical workflow entails.
- Coverage of machine learning techniques and algorithms. Are a variety of techniques (e.g. regression, classification, clustering, etc.) and algorithms (e.g. within classification: naive Bayes, decision trees, support vector machines, etc.) covered or just a select few? Preference is given to courses that cover more without skimping on detail.
- Usage of common data science and machine learning tools. Is the course taught using popular programming languages like Python, R, and/or Scala? How about popular libraries within those languages? These aren’t necessary, but helpful so slight preference is given to these courses.
What is machine learning? What is a workflow?
A popular definition originates from Arthur Samuel in 1959: machine learning is a subfield of computer science that gives “computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.”
In practice, this means developing computer programs that can make
predictions based on data. Just as humans can learn from experience, so
can computers, where data = experience.
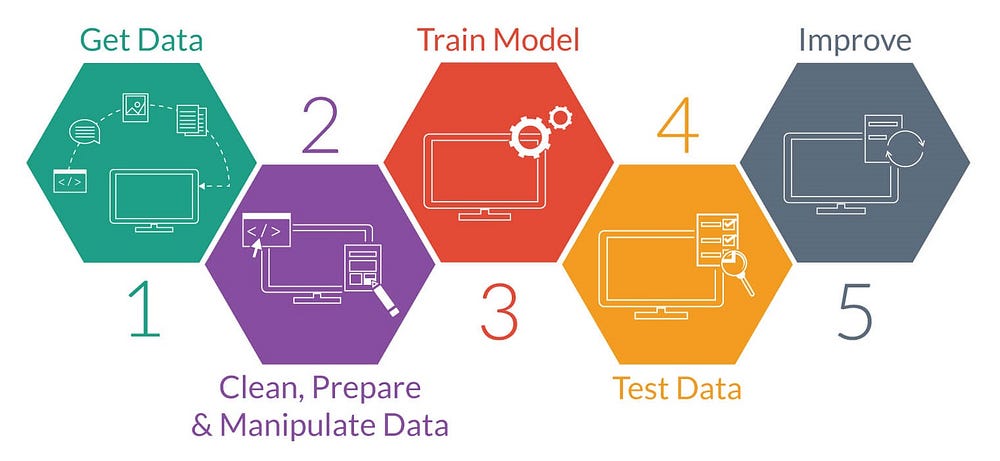
A
machine learning workflow is the process required for carrying out a
machine learning project. Though individual projects can differ, most
workflows share several common tasks: problem evaluation, data
exploration, data preprocessing, model training/testing/deployment, etc.
Below you’ll find helpful visualization of these core steps:
The
ideal course introduces the entire process and provides interactive
examples, assignments, and/or quizzes where students can perform each
task themselves.
Do these courses cover deep learning?
First off, let’s define deep learning. Here is a succinct description:
“Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning concerned with algorithms inspired by the structure and function of the brain called artificial neural networks.”
— Jason Brownlee from Machine Learning Mastery
As
would be expected, portions of some of the machine learning courses
contain deep learning content. I chose not to include deep learning-only
courses, however. If you are interested in deep learning specifically,
we’ve got you covered with the following article:
My top three recommendations from that list would be:
- Creative Applications of Deep Learning with TensorFlow by Kadenze
- Neural Networks for Machine Learning by the University of Toronto (taught by Geoffrey Hinton) via Coursera
- Deep Learning A-Z™: Hands-On Artificial Neural Networks
by Kirill Eremenko, Hadelin de Ponteves, and the SuperDataScience Team via Udemy
Recommended prerequisites
Several
courses listed below ask students to have prior programming, calculus,
linear algebra, and statistics experience. These prerequisites are
understandable given that machine learning is an advanced discipline.
Missing
a few subjects? Good news! Some of this experience can be acquired
through our recommendations in the first two articles (programming, statistics)
of this Data Science Career Guide. Several top-ranked courses below
also provide gentle calculus and linear algebra refreshers and highlight
the aspects most relevant to machine learning for those less familiar.
Our pick for the best machine learning course is…
- Machine Learning (Stanford University via Coursera)
Stanford University’s Machine Learning
on Coursera is the clear current winner in terms of ratings, reviews,
and syllabus fit. Taught by the famous Andrew Ng, Google Brain founder
and former chief scientist at Baidu, this was the class that sparked the founding of Coursera. It has a 4.7-star weighted average rating over 422 reviews.
Released
in 2011, it covers all aspects of the machine learning workflow. Though
it has a smaller scope than the original Stanford class upon which it
is based, it still manages to cover a large number of techniques and
algorithms. The estimated timeline is eleven weeks, with two weeks
dedicated to neural networks and deep learning. Free and paid options
are available.
Ng
is a dynamic yet gentle instructor with a palpable experience. He
inspires confidence, especially when sharing practical implementation
tips and warnings about common pitfalls. Though the course doesn’t dive
too deep into the underlying math, both reviewers with technical and
non-technical backgrounds enjoyed the learning experience. A linear
algebra refresher is provided and Ng highlights the aspects of calculus
most relevant to machine learning.
Evaluation
is automatic and is done via multiple choice quizzes that follow each
lesson and programming assignments. The assignments (there are eight of
them) can be completed in MATLAB or Octave, which is an open-source
version of MATLAB. Ng explains his language choice:
In the past, I’ve tried to teach machine learning using a large variety of different programming languages including C++, Java, Python, NumPy, and also Octave … And what I’ve seen after having taught machine learning for almost a decade is that you learn much faster if you use Octave as your programming environment.
Though Python and R are likely more compelling choices in 2017 with the increased popularity of those languages, reviewers note that that shouldn’t stop you from taking the course.
A few prominent reviewers noted the following:
Of longstanding renown in the MOOC world, Stanford’s machine learning course really is the definitive introduction to this topic. The course broadly covers all of the major areas of machine learning … Prof. Ng precedes each segment with a motivating discussion and examples.
Andrew Ng is a gifted teacher and able to explain complicated subjects in a very intuitive and clear way, including the math behind all concepts. Highly recommended.
The only problem I see with this course if that it sets the expectation bar very high for other courses.

A new Ivy League introduction with a brilliant professor
- Machine Learning (Columbia University via edX)
Columbia University’s Machine Learning
is a relatively new offering that is part of their Artificial
Intelligence MicroMasters on edX. Though it is newer and doesn’t have a
large number of reviews, the ones that it does have are exceptionally
strong. Professor John Paisley is noted as brilliant, clear, and clever.
It has a 4.8-star weighted average rating over 10 reviews.
The
course also covers all aspects of the machine learning workflow and
more algorithms than the above Stanford offering. Columbia’s is a more
advanced introduction, with reviewers noting that students should be
comfortable with the recommended prerequisites (calculus, linear
algebra, statistics, probability, and coding).
Quizzes
(11), programming assignments (4), and a final exam are the modes of
evaluation. Students can use either Python, Octave, or MATLAB to
complete the assignments. The course’s total estimated timeline is eight
to ten hours per week over twelve weeks. It is free with a verified
certificate available for purchase.
Below are a few of the aforementioned sparkling reviews:
Over all my years of [being a] student I’ve come across professors who aren’t brilliant, professors who are brilliant but they don’t know how to explain the stuff clearly, and professors who are brilliant and know how explain the stuff clearly. Dr. Paisley belongs to the third group.
This is a great course … The instructor’s language is precise and that is, to my mind, one of the strongest points of the course. The lectures are of high quality and the slides are great too.
Dr. Paisley and his supervisor are … students of Michael Jordan, the father of machine learning. [Dr. Paisley] is the best ML professor at Columbia because of his ability to explain stuff clearly. Up to 240 students have selected his course this semester, the largest number among all professors [teaching] machine learning at Columbia.

A practical intro in Python & R from industry experts
- Machine Learning A-Z™: Hands-On Python & R In Data Science (Kirill Eremenko, Hadelin de Ponteves, and the SuperDataScience Team via Udemy)
Machine Learning A-Z™ on Udemy is an impressively detailed offering that provides instruction in both Python
and R, which is rare and can’t be said for any of the other top
courses. It has a 4.5-star weighted average rating over 3,071 reviews,
which makes it the most reviewed course of the ones considered.
It
covers the entire machine learning workflow and an almost ridiculous
(in a good way) number of algorithms through 40.5 hours of on-demand
video. The course takes a more applied approach and is lighter math-wise
than the above two courses. Each section starts with an “intuition”
video from Eremenko that summarizes the underlying theory of the concept
being taught. de Ponteves then walks through implementation with
separate videos for both Python and R. As a “bonus,” the course includes
Python and R code templates for students to download and use on their
own projects. There are quizzes and homework challenges, though these
aren’t the strong points of the course.
Eremenko
and the SuperDataScience team are revered for their ability to “make
the complex simple.” Also, the prerequisites listed are “just some high
school mathematics,” so this course might be a better option for those
daunted by the Stanford and Columbia offerings.
A few prominent reviewers noted the following:
The course is professionally produced, the sound quality is excellent, and the explanations are clear and concise … It’s an incredible value for your financial and time investment.
It was spectacular to be able to follow the course in two different programming languages simultaneously.
Kirill is one of the absolute best instructors on Udemy (if not the Internet) and I recommend taking any class he teaches. … This course has a ton of content, like a ton!

The competition
Our
#1 pick had a weighted average rating of 4.7 out of 5 stars over 422
reviews. Let’s look at the other alternatives, sorted by descending
rating. A reminder that deep learning-only courses are not included in
this guide — you can find those here.
The Analytics Edge
(Massachusetts Institute of Technology/edX): More focused on analytics
in general, though it does cover several machine learning topics. Uses
R. Strong narrative that leverages familiar real-world examples.
Challenging. Ten to fifteen hours per week over twelve weeks. Free with a
verified certificate available for purchase. It has a 4.9-star weighted
average rating over 214 reviews.
Python for Data Science and Machine Learning Bootcamp
(Jose Portilla/Udemy): Has large chunks of machine learning content,
but covers the whole data science process. More of a very detailed intro
to Python. Amazing course, though not ideal for the scope of this
guide. 21.5 hours of on-demand video. Cost varies depending on Udemy
discounts, which are frequent. It has a 4.6-star weighted average rating
over 3316 reviews.
Data Science and Machine Learning Bootcamp with R
(Jose Portilla/Udemy): The comments for Portilla’s above course apply
here as well, except for R. 17.5 hours of on-demand video. Cost varies
depending on Udemy discounts, which are frequent. It has a 4.6-star
weighted average rating over 1317 reviews.
Machine Learning Series
(Lazy Programmer Inc./Udemy): Taught by a data scientist/big data
engineer/full stack software engineer with an impressive resume, Lazy
Programmer currently has a series of 16 machine learning-focused courses
on Udemy. In total, the courses have 5000+ ratings and almost all of
them have 4.6 stars. A useful course ordering is provided in each
individual course’s description. Uses Python. Cost varies depending on
Udemy discounts, which are frequent.
Machine Learning
(Georgia Tech/Udacity): A compilation of what was three separate
courses: Supervised, Unsupervised and Reinforcement Learning. Part of
Udacity’s Machine Learning Engineer Nanodegree and Georgia Tech’s Online
Master’s Degree (OMS). Bite-sized videos, as is Udacity’s style.
Friendly professors. Estimated timeline of four months. Free. It has a
4.56-star weighted average rating over 9 reviews.
Implementing Predictive Analytics with Spark in Azure HDInsight
(Microsoft/edX): Introduces the core concepts of machine learning and a
variety of algorithms. Leverages several big data-friendly tools,
including Apache Spark, Scala, and Hadoop. Uses both Python and R. Four
hours per week over six weeks. Free with a verified certificate
available for purchase. It has a 4.5-star weighted average rating over 6
reviews.
Data Science and Machine Learning with Python — Hands On!
(Frank Kane/Udemy): Uses Python. Kane has nine years of experience at
Amazon and IMDb. Nine hours of on-demand video. Cost varies depending on
Udemy discounts, which are frequent. It has a 4.5-star weighted average
rating over 4139 reviews.
Scala and Spark for Big Data and Machine Learning
(Jose Portilla/Udemy): “Big data” focus, specifically on implementation
in Scala and Spark. Ten hours of on-demand video. Cost varies depending
on Udemy discounts, which are frequent. It has a 4.5-star weighted
average rating over 607 reviews.
Machine Learning Engineer Nanodegree
(Udacity): Udacity’s flagship Machine Learning program, which features a
best-in-class project review system and career support. The program is a
compilation of several individual Udacity courses, which are free.
Co-created by Kaggle. Estimated timeline of six months. Currently costs
$199 USD per month with a 50% tuition refund available for those who
graduate within 12 months. It has a 4.5-star weighted average rating
over 2 reviews.
Learning From Data (Introductory Machine Learning)
(California Institute of Technology/edX): Enrollment is currently
closed on edX, but is also available via CalTech’s independent platform
(see below). It has a 4.49-star weighted average rating over 42 reviews.
Learning From Data (Introductory Machine Learning)
(Yaser Abu-Mostafa/California Institute of Technology): “A real Caltech
course, not a watered-down version.” Reviews note it is excellent for
understanding machine learning theory. The professor, Yaser Abu-Mostafa,
is popular among students and also wrote the textbook upon which this
course is based. Videos are taped lectures (with lectures slides
picture-in-picture) uploaded to YouTube. Homework assignments are .pdf
files. The course experience for online students isn’t as polished as
the top three recommendations. It has a 4.43-star weighted average
rating over 7 reviews.
Mining Massive Datasets
(Stanford University): Machine learning with a focus on “big data.”
Introduces modern distributed file systems and MapReduce. Ten hours per
week over seven weeks. Free. It has a 4.4-star weighted average rating
over 30 reviews.
AWS Machine Learning: A Complete Guide With Python
(Chandra Lingam/Udemy): A unique focus on cloud-based machine learning
and specifically Amazon Web Services. Uses Python. Nine hours of
on-demand video. Cost varies depending on Udemy discounts, which are
frequent. It has a 4.4-star weighted average rating over 62 reviews.
Introduction to Machine Learning & Face Detection in Python
(Holczer Balazs/Udemy): Uses Python. Eight hours of on-demand video.
Cost varies depending on Udemy discounts, which are frequent. It has a
4.4-star weighted average rating over 162 reviews.
StatLearning: Statistical Learning (Stanford University): Based on the excellent textbook, “An Introduction to Statistical Learning, with Applications in R”
and taught by the professors who wrote it. Reviewers note that the MOOC
isn’t as good as the book, citing “thin” exercises and mediocre videos.
Five hours per week over nine weeks. Free. It has a 4.35-star weighted
average rating over 84 reviews.
Machine Learning Specialization
(University of Washington/Coursera): Great courses, but last two
classes (including the capstone project) were canceled. Reviewers note
that this series is more digestable (read: easier for those without
strong technical backgrounds) than other top machine learning courses
(e.g. Stanford’s or Caltech’s). Be aware that the series is incomplete
with recommender systems, deep learning, and a summary missing. Free and
paid options available. It has a 4.31-star weighted average rating over
80 reviews.

From 0 to 1: Machine Learning, NLP & Python-Cut to the Chase
(Loony Corn/Udemy): “A down-to-earth, shy but confident take on machine
learning techniques.” Taught by four-person team with decades of
industry experience together. Uses Python. Cost varies depending on
Udemy discounts, which are frequent. It has a 4.2-star weighted average
rating over 494 reviews.
Principles of Machine Learning
(Microsoft/edX): Uses R, Python, and Microsoft Azure Machine Learning.
Part of the Microsoft Professional Program Certificate in Data Science.
Three to four hours per week over six weeks. Free with a verified
certificate available for purchase. It has a 4.09-star weighted average
rating over 11 reviews.
Big Data: Statistical Inference and Machine Learning
(Queensland University of Technology/FutureLearn): A nice, brief
exploratory machine learning course with a focus on big data. Covers a
few tools like R, H2O Flow, and WEKA. Only three weeks in duration at a
recommended two hours per week, but one reviewer noted that six hours
per week would be more appropriate. Free and paid options available. It
has a 4-star weighted average rating over 4 reviews.
Genomic Data Science and Clustering
(Bioinformatics V) (University of California, San Diego/Coursera): For
those interested in the intersection of computer science and biology and
how it represents an important frontier in modern science. Focuses on
clustering and dimensionality reduction. Part of UCSD’s Bioinformatics
Specialization. Free and paid options available. It has a 4-star
weighted average rating over 3 reviews.
Intro to Machine Learning
(Udacity): Prioritizes topic breadth and practical tools (in Python)
over depth and theory. The instructors, Sebastian Thrun and Katie
Malone, make this class so fun. Consists of bite-sized videos and
quizzes followed by a mini-project for each lesson. Currently part of
Udacity’s Data Analyst Nanodegree. Estimated timeline of ten weeks.
Free. It has a 3.95-star weighted average rating over 19 reviews.
Machine Learning for Data Analysis
(Wesleyan University/Coursera): A brief intro machine learning and a
few select algorithms. Covers decision trees, random forests, lasso
regression, and k-means clustering. Part of Wesleyan’s Data Analysis and
Interpretation Specialization. Estimated timeline of four weeks. Free
and paid options available. It has a 3.6-star weighted average rating
over 5 reviews.
Programming with Python for Data Science
(Microsoft/edX): Produced by Microsoft in partnership with Coding Dojo.
Uses Python. Eight hours per week over six weeks. Free and paid options
available. It has a 3.46-star weighted average rating over 37 reviews.
Machine Learning for Trading
(Georgia Tech/Udacity): Focuses on applying probabilistic machine
learning approaches to trading decisions. Uses Python. Part of Udacity’s
Machine Learning Engineer Nanodegree and Georgia Tech’s Online Master’s
Degree (OMS). Estimated timeline of four months. Free. It has a
3.29-star weighted average rating over 14 reviews.
Practical Machine Learning
(Johns Hopkins University/Coursera): A brief, practical introduction to
a number of machine learning algorithms. Several one/two-star reviews
expressing a variety of concerns. Part of JHU’s Data Science
Specialization. Four to nine hours per week over four weeks. Free and
paid options available. It has a 3.11-star weighted average rating over
37 reviews.
Machine Learning for Data Science and Analytics
(Columbia University/edX): Introduces a wide range of machine learning
topics. Some passionate negative reviews with concerns including content
choices, a lack of programming assignments, and uninspiring
presentation. Seven to ten hours per week over five weeks. Free with a
verified certificate available for purchase. It has a 2.74-star weighted
average rating over 36 reviews.
Recommender Systems Specialization (University
of Minnesota/Coursera): Strong focus one specific type of machine
learning — recommender systems. A four course specialization plus a
capstone project, which is a case study. Taught using LensKit (an
open-source toolkit for recommender systems). Free and paid options
available. It has a 2-star weighted average rating over 2 reviews.
Machine Learning With Big Data
(University of California, San Diego/Coursera): Terrible reviews that
highlight poor instruction and evaluation. Some noted it took them mere
hours to complete the whole course. Part of UCSD’s Big Data
Specialization. Free and paid options available. It has a 1.86-star
weighted average rating over 14 reviews.
Practical Predictive Analytics: Models and Methods
(University of Washington/Coursera): A brief intro to core machine
learning concepts. One reviewer noted that there was a lack of quizzes
and that the assignments were not challenging. Part of UW’s Data Science
at Scale Specialization. Six to eight hours per week over four weeks.
Free and paid options available. It has a 1.75-star weighted average
rating over 4 reviews.
The following courses had one or no reviews as of May 2017.
Machine Learning for Musicians and Artists
(Goldsmiths, University of London/Kadenze): Unique. Students learn
algorithms, software tools, and machine learning best practices to make
sense of human gesture, musical audio, and other real-time data. Seven
sessions in length. Audit (free) and premium ($10 USD per month) options
available. It has one 5-star review.
Applied Machine Learning in Python
(University of Michigan/Coursera): Taught using Python and the scikit
learn toolkit. Part of the Applied Data Science with Python
Specialization. Scheduled to start May 29th. Free and paid options
available.
Applied Machine Learning
(Microsoft/edX): Taught using various tools, including Python, R, and
Microsoft Azure Machine Learning (note: Microsoft produces the course).
Includes hands-on labs to reinforce the lecture content. Three to four
hours per week over six weeks. Free with a verified certificate
available for purchase.
Machine Learning for Data Science
(University of California, San Diego/edX): Doesn’t launch until January
2018. Programming examples and assignments are in Python, using Jupyter
notebooks. Eight hours per week over ten weeks. Free with a verified
certificate available for purchase.
Introduction to Analytics Modeling
(Georgia Tech/edX): The course advertises R as its primary programming
tool. Five to ten hours per week over ten weeks. Free with a verified
certificate available for purchase.
Predictive Analytics: Gaining Insights from Big Data
(Queensland University of Technology/FutureLearn): Brief overview of a
few algorithms. Uses Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s Vertica Analytics
platform as an applied tool. Start date to be announced. Two hours per
week over four weeks. Free with a Certificate of Achievement available
for purchase.
Introducción al Machine Learning
(Universitas Telefónica/Miríada X): Taught in Spanish. An introduction
to machine learning that covers supervised and unsupervised learning. A
total of twenty estimated hours over four weeks.
Machine Learning Path Step
(Dataquest): Taught in Python using Dataquest’s interactive in-browser
platform. Multiple guided projects and a “plus” project where you build
your own machine learning system using your own data. Subscription
required.
The following six courses are offered by DataCamp.
DataCamp’s hybrid teaching style leverages video and text-based
instruction with lots of examples through an in-browser code editor. A
subscription is required for full access to each course.

Introduction to Machine Learning
(DataCamp): Covers classification, regression, and clustering
algorithms. Uses R. Fifteen videos and 81 exercises with an estimated
timeline of six hours.
Supervised Learning with scikit-learn
(DataCamp): Uses Python and scikit-learn. Covers classification and
regression algorithms. Seventeen videos and 54 exercises with an
estimated timeline of four hours.
Unsupervised Learning in R
(DataCamp): Provides a basic introduction to clustering and
dimensionality reduction in R. Sixteen videos and 49 exercises with an
estimated timeline of four hours.
Machine Learning Toolbox
(DataCamp): Teaches the “big ideas” in machine learning. Uses R. 24
videos and 88 exercises with an estimated timeline of four hours.
Machine Learning with the Experts: School Budgets
(DataCamp): A case study from a machine learning competition on
DrivenData. Involves building a model to automatically classify items in
a school’s budget. DataCamp’s “Supervised Learning with scikit-learn”
is a prerequisite. Fifteen videos and 51 exercises with an estimated
timeline of four hours.
Unsupervised Learning in Python
(DataCamp): Covers a variety of unsupervised learning algorithms using
Python, scikit-learn, and scipy. The course ends with students building a
recommender system to recommend popular musical artists. Thirteen
videos and 52 exercises with an estimated timeline of four hours.
Machine Learning
(Tom Mitchell/Carnegie Mellon University): Carnegie Mellon’s graduate
introductory machine learning course. A prerequisite to their second
graduate level course, “Statistical Machine Learning.” Taped university
lectures with practice problems, homework assignments, and a midterm
(all with solutions) posted online. A 2011 version
of the course also exists. CMU is one of the best graduate schools for
studying machine learning and has a whole department dedicated to ML.
Free.
Statistical Machine Learning
(Larry Wasserman/Carnegie Mellon University): Likely the most advanced
course in this guide. A follow-up to Carnegie Mellon’s Machine Learning
course. Taped university lectures with practice problems, homework
assignments, and a midterm (all with solutions) posted online. Free.

Undergraduate Machine Learning
(Nando de Freitas/University of British Columbia): An undergraduate
machine learning course. Lectures are filmed and put on YouTube with the
slides posted on the course website. The course assignments are posted
as well (no solutions, though). de Freitas is now a full-time professor
at the University of Oxford and receives praise for his teaching
abilities in various forums. Graduate version available (see below).
Machine Learning
(Nando de Freitas/University of British Columbia): A graduate machine
learning course. The comments in de Freitas’ undergraduate course
(above) apply here as well.
Wrapping it Up
This
is the fifth of a six-piece series that covers the best online courses
for launching yourself into the data science field. We covered
programming in the first article, statistics and probability in the second article, intros to data science in the third article, and data visualization in the fourth.
The
final piece will be a summary of those articles, plus the best online
courses for other key topics such as data wrangling, databases, and even
software engineering.
If you’re looking for a complete list of Data Science online courses, you can find them on Class Central’s Data Science and Big Data subject page.
If you enjoyed reading this, check out some of Class Central’s other pieces:
If you have suggestions for courses I missed, let me know in the responses!
If you found this helpful, click the 💚 so more people will see it here on Medium.
This is a condensed version of my original article published on Class Central, where I’ve included detailed course syllabi.
No comments:
Post a Comment